Module Architecture
The Bibliotheca stack has been crafted to take advantage of Ethereum's capability to facilitate composability between smart contracts. The financial lego blocks of DeFi demonstrated the enhancements composability provides both to developers and users, such as the ablility to bootstrap complex financial applications and having standards to trade between assets.
Feature rich gaming applications proved to require too much computation for the L1 network to be viable, however we believe StarkNet will provide a new paradigm of development allowing the benefits of composability to be applied to gaming ecosystems. These extend beyond simply being able to share a PFP between games or trade one games' asset for another - but rather deeply integrated gaming experiences developed in a more decentralized fashion. The open nature of the blockchain allows developers to build on top of each other and integrate applications - leading to the emergence of standards encompassing concepts such as shared XP upgrades, physics and verifiable randomness.
Modules act as open source DLCs
Bibliotheca takes advantage of smart contract composability by modularizing its codebase into reusable and replaceable functional units called modules. The functional units are defined as smart contracts that encapsulate specific functionality of the game and interact with other smart contracts through well-defined interfaces. The functional units can be combined in different ways to form new games or applications, or they can be replaced with new versions that implement the same functionality but with different performance, security, or cost characteristics.
The functional units can also be integrated with external systems, such as Oracles, through standard protocols, such as ERC-20, ERC-721, ERC-1155 and others. This approach allows for a more efficient and flexible development process, as well as a more robust and secure system, as it enables the separation of concerns, the isolation of bugs, the independent scaling, and the independent upgrade of each functional unit.
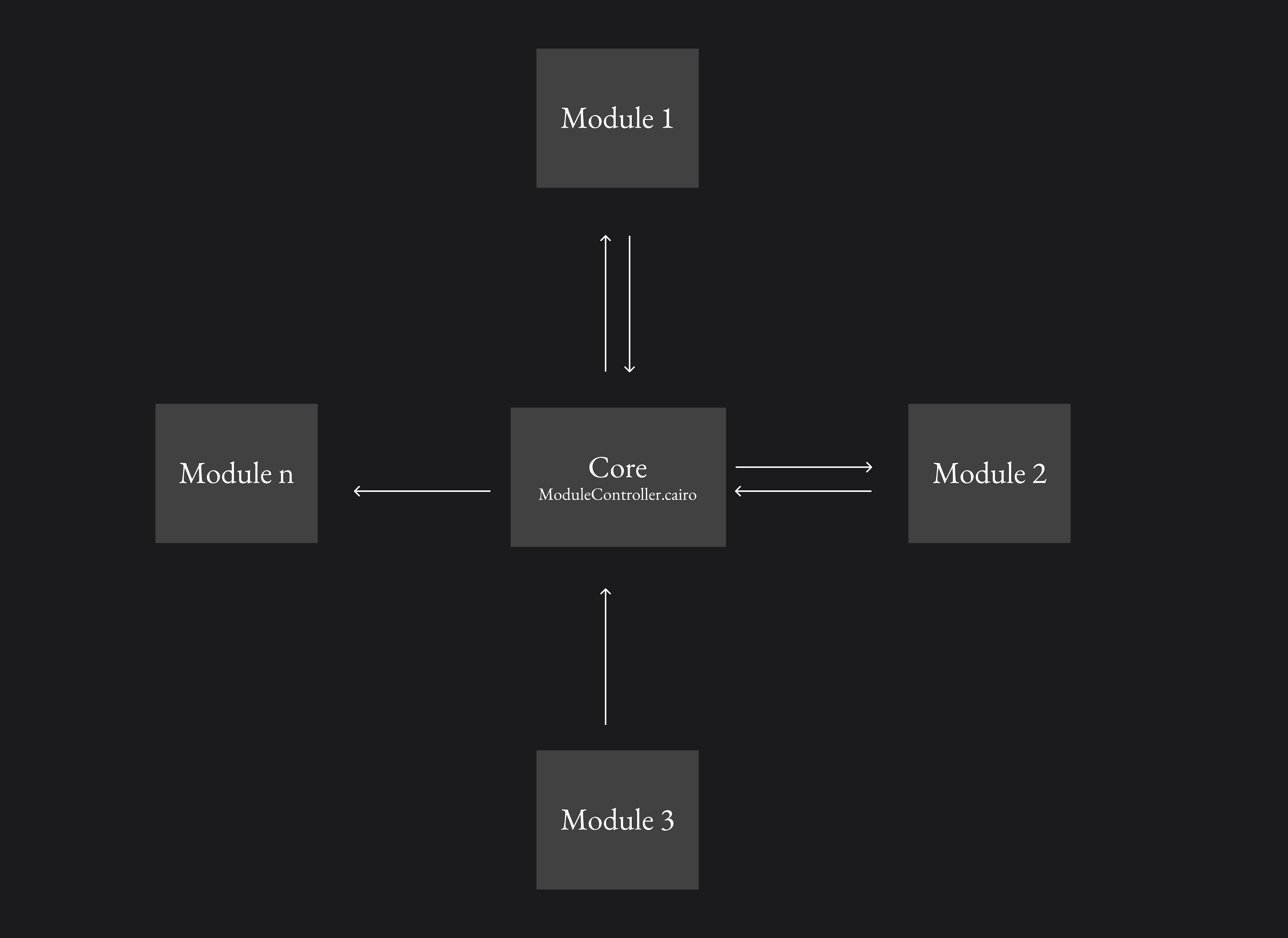
The core game logic and state is controlled by a module controller contract which determines which contracts have the ability to write to the game state and logic. This centralizes control and allows for a more secure and manageable system. Upgrades and changes to the controller, such as adding new building types or integrating new projects, are governed by the Bibliotheca DAO. This allows for a decentralized and community-driven process for making changes to the game.
By creating a modular structure, the game has the ability to expand and evolve independent of the core development team. For example, a new developer could write a new module that interacts with the rest of the game, propose it to the community, and if it is approved through a vote, it can be added to the game. This allows for a more collaborative and open-source development process and allows for the community to drive the direction and evolution of the game.
Creators get paid
The transparency and verifiability of the blockchain allows for a unique opportunity to simulate an 'app store' experience for new developers. A developer who creates a new module for the game can choose to include a small transaction fee for its use, which would result in the developer being paid each time a player interacts with it. This creates a financial incentive for developers to create new and innovative modules that can enhance the game experience for players.